
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
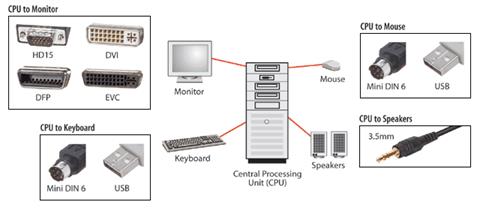
Text 3 Central Processing Unit
|
|
Read the text and retell it.
At the centre of the computer system is the CPU, which can be considered to be the “brain” of the computer. Its main components are the central processor and the main memory. The speed and capacity of these components have been greatly improved with each new generation of computers. In the first generation, the central processor was built from electronic valves, which were rather unreliable. The second generation used transistors. The third generation used integrated circuits. The fourth generation of computers uses microprocessors. These are contained on electronic chips, which are slices of silicon with thousands of electronic components and circuits engraved on them.
Early computers used magnetic cores in their main memory but fourth generation computers use much smaller and more powerful electronic memory chips.
The two parts of the central processor are the Control Unit (CU) and the arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU).
The control unit controls all other units in the computer system. It decodes the program instructions and makes sure they are carried out in the correct sequence. The arithmetic and logic unit, on the other hand, performs the calculations and data manipulation e.g. comparing, sorting and combining data.
These units have small, short-item storage areas called registers, which are used for special tasks. For example, the register in the CU known as the program computer is used to hold the address of the next instruction to be carried out. The register in the ALU known as the accumulator is used to temporarily hold the data item currently being processed.
Each unit of the CPU is connected by a group of wires called a bus. There are data buses for carrying data from one unit to another, control buses for sending control signals to each unit and address buses for accessing each part of the main memory.
— Регулярная проверка качества ссылок по более чем 100 показателям и ежедневный пересчет показателей качества проекта.
— Все известные форматы ссылок: арендные ссылки, вечные ссылки, публикации (упоминания, мнения, отзывы, статьи, пресс-релизы).
— SeoHammer покажет, где рост или падение, а также запросы, на которые нужно обратить внимание.
SeoHammer еще предоставляет технологию Буст, она ускоряет продвижение в десятки раз, а первые результаты появляются уже в течение первых 7 дней. Зарегистрироваться и Начать продвижение
The power of CPU is partly determined by its speed. This is controlled by a clock in the processor, which sends out regular pulses to each unit to keep them in step. The clock pulse rate is measured in megahertz (MHz).
|
|
