
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Aircraft
|
|

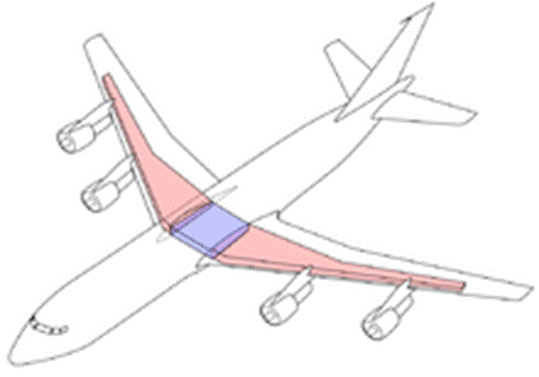
Layout of a modern airliner's main fuel tanks
Aircraft typically use three types of fuel tanks: integral, rigid removable, and bladder.
· Integral tanks are areas inside the aircraft structure that have been sealed to allow fuel storage. An example of this type is the " wet wing" commonly used in larger aircraft. Since these tanks are part of the aircraft structure, they cannot be removed for service or inspection. Inspection panels must be provided to allow internal inspection, repair, and overall servicing of the tank. Most large transport aircraft use this system, storing fuel in the wings, belly, and sometimes tail of the airplane.
· Rigid removable tanks are installed in a compartment designed to accommodate the tank. They are typically of metal construction, and may be removed for inspection, replacement, or repair. The aircraft does not rely on the tank for structural integrity. These tanks are commonly found in smaller general aviation aircraft, such as the Cessna 172.
· Bladder tanks, or fuel cells, [5] are reinforced rubberized bags installed in a section of aircraft structure designed to accommodate the weight of the fuel. The bladder is rolled up and installed into the compartment through the fuel filler neck or access panel, and is secured by means of metal buttons or snaps inside the compartment. Many high-performance light aircraft, helicopters and some smaller turboprops use bladder tanks. One major down-side to this type of tank is the tendency for materials to work harden through extensive use making them brittle causing cracks. One major plus side is the ability to utilise as much of the aircraft as possible to store fuel.
· Combat aircraft and helicopters generally use self-sealing fuel tanks.
· 
Fuel tanks have been implicated in aviation disasters, being the cause of the accident or worsening it (fuel tank explosion). For example:
· The official explanation for the explosion and subsequent crash of TWA Flight 800 is that an explosive fuel/air mixture was created in one of the aircraft's fuel tanks. Faulty wiring then provided an ignition source within the tank, destroying the airliner. While the accuracy of the official findings is still questioned in this case, similar explosions have occurred in other aircraft. It is possible to reduce the chance of fuel tank explosions by a fuel tank inerting system or fire-fighting foam in the tanks.[7]
· Burning fuel can explode or set fire to the same airplane or adjacent objects and people. In the 1960 Munich Convair 340 crash, a transport crashed into a major street. Burning fuel set fire to a tramcar. All 20 people aboard the plane and 32 passengers of the tram died.[8]
In some areas, notably the USA, an aircraft's fuel tank is also referred to, slightly confusingly, as an aircraft fuel cell.
Water supply[edit]
Water supply systems can have primary or backup power supplied by diesel-fueled generators fed by a small " day tank" and a much larger bulk storage fuel tank.
Safety
Proper design and construction of a fuel tank play a major role in the safety of the system of which the tank is a part. In most cases intact fuel tanks are very safe, as the tank is full of fuel vapour/air mixture that is well above the flammability limits, and thus cannot burn even if an ignition source were present (which is rare).
Bunded oil tanks are used for safely storing domestic heating oil and other hazardous materials. Bunding is often required by insurance companies, rather than single skinned oil storage tanks.
Several systems, such as BattleJacket and rubber bladders, have been developed and deployed for use in protecting (from explosion caused by enemy fire) the fuel tanks of military vehicles in conflict zones.




|
|