
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Molecules and energy
|
|
|
| Hydrogen |
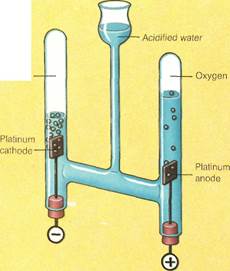
When a current passes through water, the energy from the electricity breaks the water molecules apart into hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The atoms of each type then combine to form diatomic molecules of hydrogen and oxygen. A diatomic molecule contains two atoms. Thus, a diatomic molecule of hydrogen has two atoms of hydrogen (H2). A diatomic mole-
cule of oxygen has two atoms of oxygen (02). Both these substances are gases at ordinary temperatures. A spark applied to a mixture of the two gases triggers off a reaction between them. This reaction makes the gases reform into water molecules. During this reaction, energy in the form of light, heat, and sound is released.
In chemical terms, a reaction occurs spontaneously only if the products are chemically more stable than the reactants. In other words, the products have to be less energetic than the reactants. The reactants are the substances that react and change into the products. Several factors contribute to the energy of a molecule. Thus, a spontaneous reaction does not always liberate energy in a recognizable form, such as light and heat. Nevertheless, many reactions do give off large quantities of usable energy. When natural gas burns, for example, its molecules react with oxygen. This releases energy that we can use to heat our homes and cook our food.
Anyone who has seen gas burning realizes that energy is released in the process. But can we call it spontaneous? The gas does not start burning by itself. Only when air is mixed with the gas and a spark or match is applied does the reaction occur. Why is this?
When a reaction takes place, chemical bonds are broken and new ones formed. In the case of the electric current passing through water (electrolysis), the bonds between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in water break. New bonds form between pairs of hydrogen atoms and pairs of oxygen atoms. Natural gas consists mainly of the hydrocarbon methane. This is a molecule containing one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen. When the bonds between the carbon and hydrogen break, new bonds are formed. The carbon combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. The hydrogen combines with oxygen to form water.
— Регулярная проверка качества ссылок по более чем 100 показателям и ежедневный пересчет показателей качества проекта.
— Все известные форматы ссылок: арендные ссылки, вечные ссылки, публикации (упоминания, мнения, отзывы, статьи, пресс-релизы).
— SeoHammer покажет, где рост или падение, а также запросы, на которые нужно обратить внимание.
SeoHammer еще предоставляет технологию Буст, она ускоряет продвижение в десятки раз, а первые результаты появляются уже в течение первых 7 дней. Зарегистрироваться и Начать продвижение
What happens in a chemical reaction is similar to a mathematical equation. In an equation, both sides of the equal sign must balance. So also in a reaction, the " before" and " after" must contain the same number and types of atoms, though differently connected.
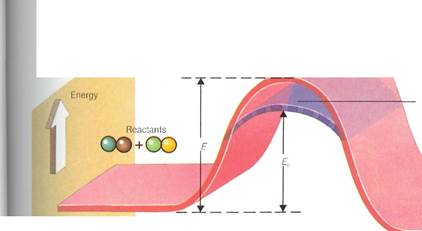
However, a chemical reaction is a bit more complicated than a mathematical equation. What generally happens is that an intermediate or transition state forms. Intermediates are usually very unstable and cannot be isolated. They break down rapidly, either back to the starting materials or into the products of the reaction. They are so unstable because they are more energetic than either the reactants or the products. To form them, it is usually necessary to supply energy to a reaction.
Once started, a reaction also releases energy. This means that a few molecules have to get sufficient energy to reach the transition state. They then release more energy as they break down into other products. This energy forms more of the transitional species and keeps the process going, if the reaction releases a lot of energy, then a very small trigger can be enough to cause an explosively fast re-
Atoms, elements, and molecules: Key chemical reactions 17

|
Many of the chemical reactions important to today's industry originally took place millions of years ago. In the potash mine, more than 3, 000 feet (915 meters) beneath the North Sea, a mechanical digger grinds out ancient deposits of potassium chloride. This chemical compound is an essential ingredient of artificial fertilizers. Potash is the commercial name of a salt containing potassium.
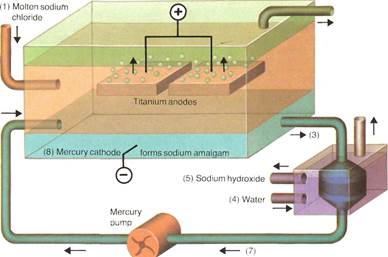
In the commercial process for producing chlorine, molten sodium chloride (1) is electrolyzed. This process produces the chlorine (2) and a mercury/sodium amalgam (3). Reacting the amalgam with water (4) gives sodium hydroxide (5), hydrogen (6), and mercury (7), which returns to the mercury cathode (8).

|
| (2) Chloride |
| Hydrogen |
| Mercury |
| Transition state |
| Transition state involving catalyst |
 action. An example would be a spark in a gasoline engine.
action. An example would be a spark in a gasoline engine.
— Разгрузит мастера, специалиста или компанию;
— Позволит гибко управлять расписанием и загрузкой;
— Разошлет оповещения о новых услугах или акциях;
— Позволит принять оплату на карту/кошелек/счет;
— Позволит записываться на групповые и персональные посещения;
— Поможет получить от клиента отзывы о визите к вам;
— Включает в себя сервис чаевых.
Для новых пользователей первый месяц бесплатно. Зарегистрироваться в сервисе
On the other hand, if you apply a spark to a piece of paper, there is not sufficient energy to make the reaction self-sustaining. But apply a lighted match and a reaction has begun. For once the paper has caught fire, it continues to burn steadily. As they react with oxygen, the molecules in paper release enough energy to make a few more molecules react. But this does not happen so quickly that the reaction occurs explosively fast.
| E — Activation energy E. — Catalyzed activation energy |
The idea of the transition state between re-actants and products helps to explain why reactions are reversible. If enough energy is supplied to the starting materials (reactants) of a reaction, they are able to reach the transition state. It is always possible for an intermediate (transition) species to break down into either
Products
oo+oo
##
Initiating a chemical reaction generally requires enough energy for some of the reactants to form an intermediate stage called a transition state. The reaction can then proceed. The overall energy content of the products is less than that of the reactants. A catalyst can have the effect of lowering the amount of energy required to start the reaction (activation energy). This makes the reaction proceed more readily.
Reaction course
18 Atoms, elements, and molecules: Key chemical reactions

|
Michael Faraday, shown here working in his laboratory, was one of the first great experimental chemists. He formulated the laws of electrolysis, discovered benzene and other organic substances, and first demonstrated the use of platinum as a catalyst.

 Nitrogen has many oxides (compounds with oxygen) and hydrides (compounds with hydrogen). It demonstrates a wide range of oxidation states, from +5 in dinitrogen pentoxideto —3 in ammonia. This diagram also illustrates the shapes of the various molecules. Brown is a nitrogen atom, red an oxygen atom, and yellow a hydrogen atom.
Nitrogen has many oxides (compounds with oxygen) and hydrides (compounds with hydrogen). It demonstrates a wide range of oxidation states, from +5 in dinitrogen pentoxideto —3 in ammonia. This diagram also illustrates the shapes of the various molecules. Brown is a nitrogen atom, red an oxygen atom, and yellow a hydrogen atom.
reactants or products. However, energy can be dissipated during a reaction. For example, heat can be given off. In such a case, lower-energy products find it difficult to reform intermediate species. In other words, it is difficult to make the reaction reversible. However, if energy is being constantly supplied, the reverse is true. For example, when a piece of iron is left in the open, it gradually turns to rust—iron oxide. But when large quantities of iron oxide are heated with other materials in a smelting furnace, the product is metallic iron. Under the constant supply of energy (heat), the reaction that turned the iron into rust is reversed.
|
|
