
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
⚡️ Для новых пользователей первый месяц бесплатно. А далее 290 руб/мес, это в 3 раза дешевле аналогов. За эту цену доступен весь функционал: напоминание о визитах, чаевые, предоплаты, общение с клиентами, переносы записей и так далее.
✅ Уйма гибких настроек, которые помогут вам зарабатывать больше и забыть про чувство «что-то мне нужно было сделать».
Сомневаетесь? нажмите на текст, запустите чат-бота и убедитесь во всем сами!
Заняття 2.4
|
|
Дошкільна та Середня освіта у Великобританії
1.Read and learn the following words.
| academic education boarding schools comprehensive creative abilities infant schools junior schools middle school non-selective system selective system | академічна освіта школа-інтернат загальноосвітня творчі здібності підготовча школа молодша школа середня школа не вибіркова система вибіркова система | preparatory pre-preparatory private schools public schools to pass an examination to require to take an examination upper school | початковий до підготовчий приватні школи = private schools здати іспит вимагати здавати іспит старша школа |
2. Read and translate the text.
The British education system is confusing to natives — to the outsider it looks almost impossible to understand! Read this article and hopefully all will become clearer...
British children are require d by law to have an education until they are 16 years old. Education is compulsory, but school is not, children are not required to attend school. They could be educated at home.
Preschool learning. Children receive preschool education from the age of about 3 to 5 in nursery schools, playgroups or the receptions classes for four year olds.
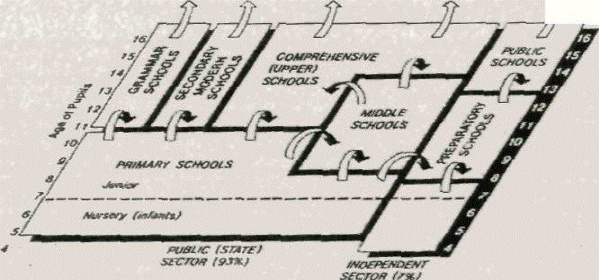
What are the main types of schools in England and Wales? There are many different types of school in Britain. There are however, only three main systems: comprehensive, elective and private. Education in schools of the comprehensive and selective systems is free of charge.
 The comprehensive system. More than 90% of children who go to State schools in England and Wales go to schools in the comprehensive system – a system introduced in the 1960s. Children go to a primary (or first) school at the age of five. These are almost always mixed sex, and usually located close to the child's home. Primary schools are subdivided into infant schools (ages 5-7), and junior schools (ages 7 - 11). In infant schools children are encouraged (допомагають навчитись) to read, write and make use of numbers and develop the creative abilities. The junior school lasts four years. Children are learning Arithmetic, Reading, Composition, History, Geography, Nature study and others.
The comprehensive system. More than 90% of children who go to State schools in England and Wales go to schools in the comprehensive system – a system introduced in the 1960s. Children go to a primary (or first) school at the age of five. These are almost always mixed sex, and usually located close to the child's home. Primary schools are subdivided into infant schools (ages 5-7), and junior schools (ages 7 - 11). In infant schools children are encouraged (допомагають навчитись) to read, write and make use of numbers and develop the creative abilities. The junior school lasts four years. Children are learning Arithmetic, Reading, Composition, History, Geography, Nature study and others.
Then at the age of 11 children may go directly to the upper school — usually called the comprehensive school. Alternatively, they may go to a middle school for three or four years before going to the upper school.
The pupils of the comprehensive schools have five lessons every day, and altogether they do (= study) eleven subjects a week Religious Education, History, English, French, Maths (= an abbreviation of mathematics), Geography, Science, Information Technology, Social Education, Visual Art, Music plus Physical Education (PE). There are three terms (= periods of continuous work) in a school year and holidays at Christmas, Easter and in summer
The comprehensive system is non-selective. This means that all children go from one school to another without taking any exams, and without being selected according to their abilities.
The selective system. In some areas of Britain, you can still find a different and older system of education (introduced in 1944). This is a selective system — children are selected for certain schools according to their ability. All children go to a primary school until the age of 11. They then take an examination called the 11-plus (test of ability). Only those who are successful go to a grammar school, where they receive a high level of academic education, which can lead (привести) to the university. Grammar schools are single sexed schools. Those who fail the exam go to a secondary modern school, where they receive an education which is less academic, and more intended (призначена) to train them for a job when they leave at the age of 16. In some areas of the UK there are not many grammar schools.
The private (independent) system. About 6 % of children go to private schools. There are three levels of private school — pre-preparatory school (age 3 or 4 to 7 years) and preparatory (prep) schools (age 7 to 11 or 13 years). A preparatory school is a school to prepare pupils to go to a public school. At the age of 11 (girls) or 13 (boys) children take an examination, known as Common Entrance. If they pass, they go on to public school, where they usually remain until they are 18. Many prep and most public schools are boarding schools — the children live at the school during the school terms. Be careful — although these schools are called " public", they are, in fact, private, and it can be very expensive to send your child to such a school. Public schools educate the ruling class of England for political, diplomatic, military and religious service. The doors of Oxford and Cambridge, the best English universities, are open to the public school-leavers. The most famous public schools are Eton, Harrow and Winchester.
Within the three systems, there are several varieties of schools. For instance, you can find: schools for boys only, schools for girls only, mixed schools for boys and grits, voluntary schools — often with a religious background — such as Roman Catholic schools.
Examinations. All children in state schools are tested in English and mathematics at the ages of 7, 11 and 14, and pupils aged 11 and 14 are also tested in science.
The public examinations taken by British schoolchildren are: GCSEs (the General Certificate of Secondary Education). Pupils usually take their GCSEs at the age of 16. And it is called 'O' (Ordinary) Level. Some children take three or four, others take as many as ten or eleven. Pupils who have passed their GCSEs may remain at school for another two years and take their " A" (Advanced) level exams.
All grammar and most comprehensive schools have a sixth form, where pupils study for their " A" levels. Any student who wants to go to university needs to pass at least two or three " A" level.
EDUCATION IN ENGLAND & WALES (to age 16)
|
|
