
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
First, scan the text and then read it more carefully.
|
|
Unit 1
RAILWAY AND MOTORWAY ENGINEERING STRUCTURES
First, scan the text and then read it more carefully.
The history of civilization makes it clear that roads have been one of the most important means for the development of the world’s economy. The transportation of people, goods and freight over land was a problem until nearly 200 years ago. Trade routes crossed continents and remote areas therefore considerable time and energy has been put into the construction of roads. The wheel is clearly humanities most important contribution to solving the problem of overland transportation but its introduction brought its own technical problems. From the start of railway construction, there were difficulties when engineering temporary and permanent routes. Trunk-railways and motorways had to overcome different natural barriers such as mountain ranges, bodies of water, fast-flowing rivers, deep gorges, and depressions, as well as urban structures. People had to build railway and motorway engineering structures to provide a crossing through and over these natural and man-made barriers.
The term Railway and Motorway Engineering Structures” (R& M ES) denotes a complex of structures used for permanent motorized travel that intersects various obstacles. Some of these structures are aimed to protect the means of permanent travel against adverse environmental effects or natural calamities. This term incorporates the following structures: aqueducts, bridges, flyovers, trestles, viaducts, culverts, tunnels, galleries, and retaining walls. The function of these structures is quite different from that of civil engineering structures therefore the term does not include buildings, garages, etc. even though they are also man-made structures. Besides, there are naturally created arch formations that resemble bridges. They occur in a massive of horizontally bedded sandstone or limestone and are formed by the collapse of a cavern roof or produced by rivers or wind erosion.
The word artificial cannot relate to railway and motorway engineering structures because this word is associated with artificial building materials. However, the origin of the Russian term “ИССО” i.e. “R& M ES” relates to the idea of individuals with the highest qualification and experience, who were gifted by Nature and possessed artistic abilities. The first railway engineers were scientists, artists and builders simultaneously. They possessed profound knowledge in different fields required for the engineering and construction of railway and motorway engineering structures. According to tradition, railway engineers expressed their creative response to a particular need, or function and the surrounding environment, and demonstrated the extent of their skills in the use of materials. They used their calculations in the service of their imagination to design thoroughly functional bridgeworks that introduced an artistic element into the environment.
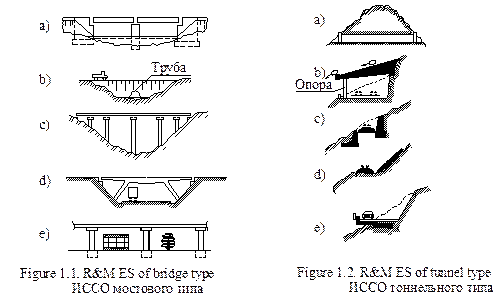
R& M ES are considered to be the most complicated and the most expensive structures. Their share ranges from 15 to 50 percent of the total capital investment in the construction of road networks. However, the length of these structures does not exceed 5% of the overall road length. Obstacles at the building site determine the R& M ES type, and there are more than 20 types of them, which can be divided into two main groups: bridge structures (fig. 1.1) and tunnel structures (fig. 1.2). A bridge is erected when the obstruction of a road is due to a river or another body of water (fig. 1.1a). If the barrier is a narrow stream or a temporary channel, it is much cheaper to build a culvert (fig. 1.1b). Railway and motorway engineering structures such as flyovers, trestles and viaducts are often confused when describing them (fig. 1.1c, d and e).
People have always been concerned with finding ways to cross gorges, canyons and ravines, which provide faster crossing for traffic and pedestrians. They build viaducts (fig. 1.1c) to reduce long distances. Grade crossings and heavy traffic flow call for overhead roads. The solution to this problem is a flyover, which provides an overhead crossing and regulates vehicle density. Trestles are built in cities where traffic flow is affected by houses, parks and industrial areas (fig. 1.1e). As a rule, trestles are rather long structures.
Tunnel works are divided into tunnels driven through mountain ranges (fig. 1.2a), and galleries located on mountain slopes (fig. 1.2b). They protect roads from rockslides, snow slips, avalanches, drifting snow, sand drift, and mudslides. Retaining walls and balconies can provide a high degree of road protection from disasters. They are less complicated R& M ES (fig. 1.2c, d, and e).
Exercises:
Give the equivalents in Russian of the following terms:
Railway and motorway engineering structures, trestle, retaining wall, gorge, railway, mudslide, water obstacle, stream, grade crossing, road protection.
|
|