
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
This can be verified by direct multiplication of the vectors and noting that due to the orthogonality of the base vectors of a rectangular system one has
|
|
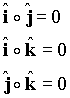
Projection of a vector onto a line:
The orthogonal projection of a vector along a line is obtained by moving one end of the vector onto the line and dropping a perpendicular onto the line from the other end of the vector. The resulting segment on the line is the vector's orthogonal projection or simply its projection.

The scalar projection of vector A along the unit vector 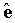 is the length of the orthogonal projection A along a line parallel to
is the length of the orthogonal projection A along a line parallel to 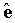 , and can be evaluated using the dot product. The relation for the projection is
, and can be evaluated using the dot product. The relation for the projection is


The vector projection of A along the unit vector  simply multiplies the scalar projection by the unit vector
simply multiplies the scalar projection by the unit vector 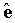 to get a vector along
to get a vector along 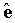 . This gives the relation
. This gives the relation
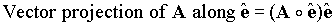
The cross product:
The cross product of vectors a and b is a vector perpendicular to both a and b and has a magnitude equal to the area of the parallelogram generated from a and b. The direction of the cross product is given by the right-hand rule. The cross product is denoted by a "  " between the vectors
" between the vectors

|
|