
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
After reading the text, prove the idea that suspension structures are the safest among bridgeworks.
|
|
Primitive people using vines for cables and mounting the roadway directly on cables constructed suspension bridges, one of the oldest of engineering forms. It is light, aesthetic, graceful and easily constructed, using materials that are easily transported. Besides, there is no danger of failure during erection because the principal carrying member - the cable - has a vast reserve of strength. It provides an economical solution to the problem of long spans over navigable streams or rivers because of its relatively small dead weight, which results from the use of cables. Since the cables are in tension, they are the most highly efficient load-carrying component. Besides the economic considerations, the suspension bridge has many other points of superiority.
Suspension and cable-stayed bridges are often confused. The reason is that they have very much in common: stiffening girders or trusses, anchor supports and cable hangers. The usual form of suspension structure consists of a flexible cable passing over two towers and anchored by backstays to a firm foundation. The roadway is suspended from the cable by means of hangers. The principal carrying element of a cable-stayed system is a flexible cable (fig. 10.1). The difference between these two bridge types is determined by the two following criteria:
1. A suspension structure has curved steel cables or chains (fig.10.1a).
2. A cable-stayed structure has cables that are straight. They are called stay cables (fig.10.1b).
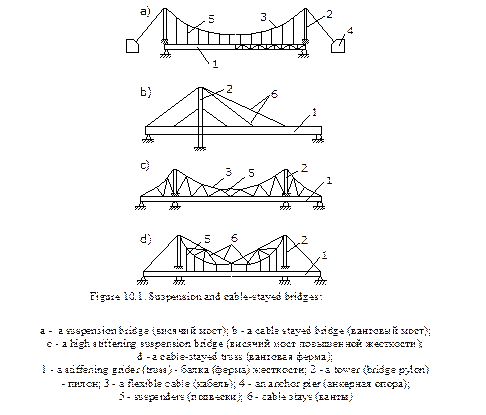
Modern bridge building uses the suspension span model on a large scale. The Akashi Kaikyo Bridge, now the world’s longest suspension bridge crosses the strait with a main span of 1, 991 m and side spans of 960 m. Its two 297 m towers, made of two hollow steel shafts connected by X-bracing, are the tallest bridge towers in the world. The two suspension cables are made of high-strength steel developed by Japanese engineers for the project. In 1995, an earthquake had its epicenter centred almost directly beneath the nearly completed Akashi Kaikyo structure; the bridge survived undamaged, though one tower shifted thus lengthening the main span by almost one metre.
The basic advantages of suspension and cable-stayed structures are:
1. The possibility to span very long distances from 500 m up to 1, 990 m.
2. High efficiency of these structures is due to the weight of the span m², which is considerably less in comparison with other bridge systems.
3. Suspension and cable-stayed bridges often have merits that are more aesthetic.
The disadvantages of suspension and cable-stayed structures are:
1. Low vertical stiffness, i.e. the structure strongly exhibits a high deflection degree under live load.
2. Low horizontal stiffness, i.e. the structure exhibits considerable displacement under the wind force in a horizontal plane.
3. High sensitivity to dynamic and aerodynamic forces.
Care must be taken to ensure that the deck does not move excessively under loading. High performance in service of suspension and cable-stayed bridges is due to the following factors:
1. Only high-strength steel wires with a rated resistance of 10, 000 MPa are used.
2. Stay cables work only in tension because working in compression may result in suspension bridge collapse.
3. No slacking in suspension bridge cable is allowed.
4. Cable hangers and stay cables support the stiffening girder at many sites.
5. The stiffening girder transmits its dead weight to the cable and the towers. Such girder’s behaviour is due to the special construction technique.
The stiffening girders distribute the load in the span and prevent distortion of the deck. To make the stiffening girder lighter the designers use the force regulation in stay cables. This results in the most acceptable distribution of force.
Exercises:
|
|