
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Read the text
|
|
Railway track substructure is a vital and essential part of the railway track system.It includes subgrade with all its drainage facilities, strengthening structures and railway engineering structures.
Subgrade is the finished surface upon which the Track is built. It is designed to have sufficient strength to support the loads passed down from the rails through the sleepers and ballast and to provide water drainage.
Before the beginning of subgrade earthworks the engineers carry out preliminary study of the area, then they perform site clearing, removal of topsoil and unsuitable material, excavation, cutting of terraces into slopes, scarifying and compaction of embankment base, provision of drainage works, sampling and testing.
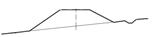
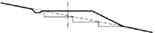
Subgrade design includes: embankment (Figure 3.2), cutting (Figure 3.3), side-hill fill (Figure 3.4), side-hill cut (Figure 3.5), side-cutting (Figure 3.6).
| 
|
| Figure 3.2 | Figure 3.3 |
|
| Figure 3.4 |

|
| Figure 3.5 |

|
| Figure 3.6 |
Embankment is a stabilized fill formation above the natural ground to a determined cross section and longitudinal profile to accommodate the railway and any associated infrastructure.
Cutting is an excavation of the natural ground to a determined cross section and longitudinal profile to accommodate the railway and any associated infrastructure.
Water is never desirable in earthworks. The service life of subgrade depends to a high degree on the quality of the drainage facilities. They include top and side drains along the railway reserve to direct surface waters away from the rail track formation to recognized water courses, pipes installed expressly to collect water from between or beside tracks and direct it away to a recognized side drain or watercourse and facilities to direct ground waters away.
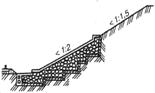
To provide subgrade stability and protection from natural effects (flood water, debris falls, snow slips, drifting snow, avalanches, sand drift, wet landslides, earthquakes, etc.) strengthening structures are made: reinforced concrete slabs (Figure 3.7), counter pilasters (Figure 3.8), ripraps (Figure 3.9), gabions (Figure 3.10), retaining walls (Figure 3.11), etc.

|
| Figure 3.7 |
|
| Figure 3.8 |

|
| Figure 3.9 |

|
| Figure 3.10 |

|
| Figure 3.11 |
Railway engineering structures – is a complex of structures used for Permanent Way at the intersection with various obstacles. The most commonly used engineering structures are bridges, culverts, trestles, viaducts, flyovers, tunnels, galleries, etc.

|
|