
Главная страница Случайная страница
Разделы сайта
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Edit] Applications in complex number theory
|
|


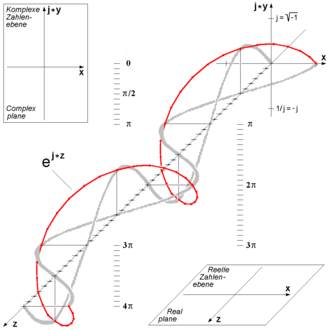

Three-dimensional visualization of Euler's formula. See also circular polarization.
This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function eix traces out the unit circle in the complex number plane as x ranges through the real numbers. Here, x is the angle that a line connecting the origin with a point on the unit circle makes with the positive real axis, measured counter clockwise and in radians.
The original proof is based on the Taylor series expansions of the exponential function ez (where z is a complex number) and of sin x and cos x for real numbers x (see below). In fact, the same proof shows that Euler's formula is even valid for all complex numbers z.
A point in the complex plane can be represented by a complex number written in cartesian coordinates. Euler's formula provides a means of conversion between cartesian coordinates and polar coordinates. The polar form simplifies the mathematics when used in multiplication or powers of complex numbers. Any complex number z = x + iy can be written as

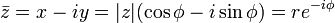
where
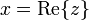 the real part
the real part
 the imaginary part
the imaginary part
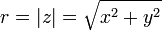 the magnitude of z
the magnitude of z
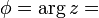 atan2 (y, x).
atan2 (y, x).
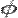 is the argument of z —i.e., the angle between the x axis and the vector z measured counterclockwise and in radians —which is defined up to addition of 2π. Many texts write tan-1(y / x) instead of atan2(y, x) but this needs adjustment when x ≤ 0.
is the argument of z —i.e., the angle between the x axis and the vector z measured counterclockwise and in radians —which is defined up to addition of 2π. Many texts write tan-1(y / x) instead of atan2(y, x) but this needs adjustment when x ≤ 0.
Now, taking this derived formula, we can use Euler's formula to define the logarithm of a complex number. To do this, we also use the definition of the logarithm (as the inverse operator of exponentiation) that
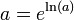
and that

both valid for any complex numbers a and b.
Therefore, one can write:
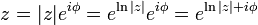
for any z ≠ 0. Taking the logarithm of both sides shows that:
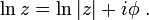
and in fact this can be used as the definition for the complex logarithm. The logarithm of a complex number is thus a multi-valued function, because ϕ is multi-valued.
Finally, the other exponential law

which can be seen to hold for all integers k, together with Euler's formula, implies several trigonometric identities as well as de Moivre's formula.
|
|